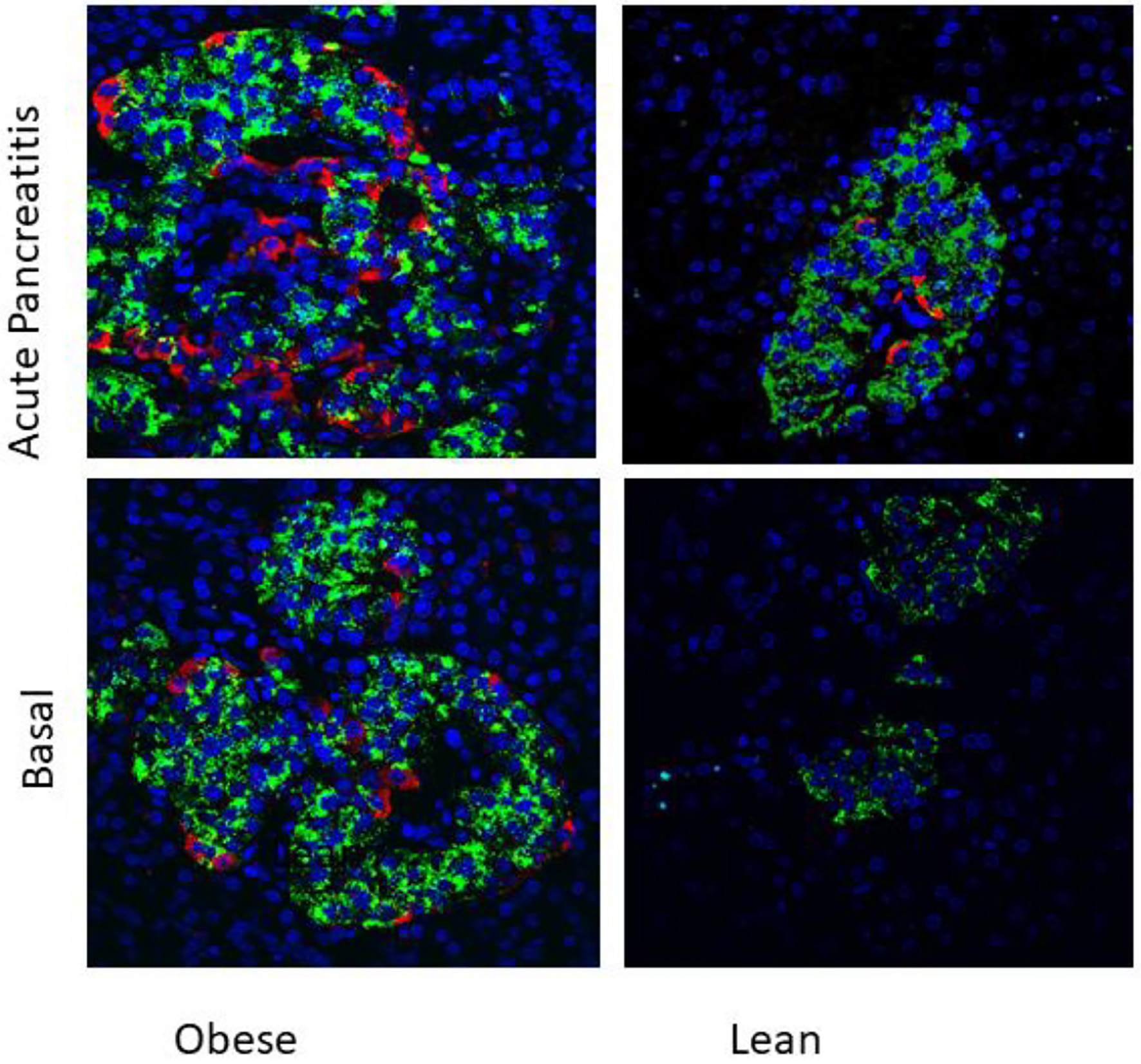
Figure 1. Immunolocalization of nestin (red) and insulin (green) in islets of 4 months old WNIN-obese and lean rats at basal conditions and after induction of acute pancreatitis (× 40). Presence of nestin-positive cells in islets of WNIN-obese rats at basal condition as well as when induced with acute pancreatitis. The induction of pancreatitis led to increased expression of nestin in these cells. Nestin-positive cells were absent in basal condition in lean rats but were present when induced with acute pancreatitis. The nestin-positive cells were localized in periphery as well as central part of islets in WNIN-obese rats. Higher pancreatic stress induced higher pancreatic stress (WNIN-obese + pancreatitis > WNIN-obese > lean + pancreatitis). Nestin was absent in islets of lean rats.
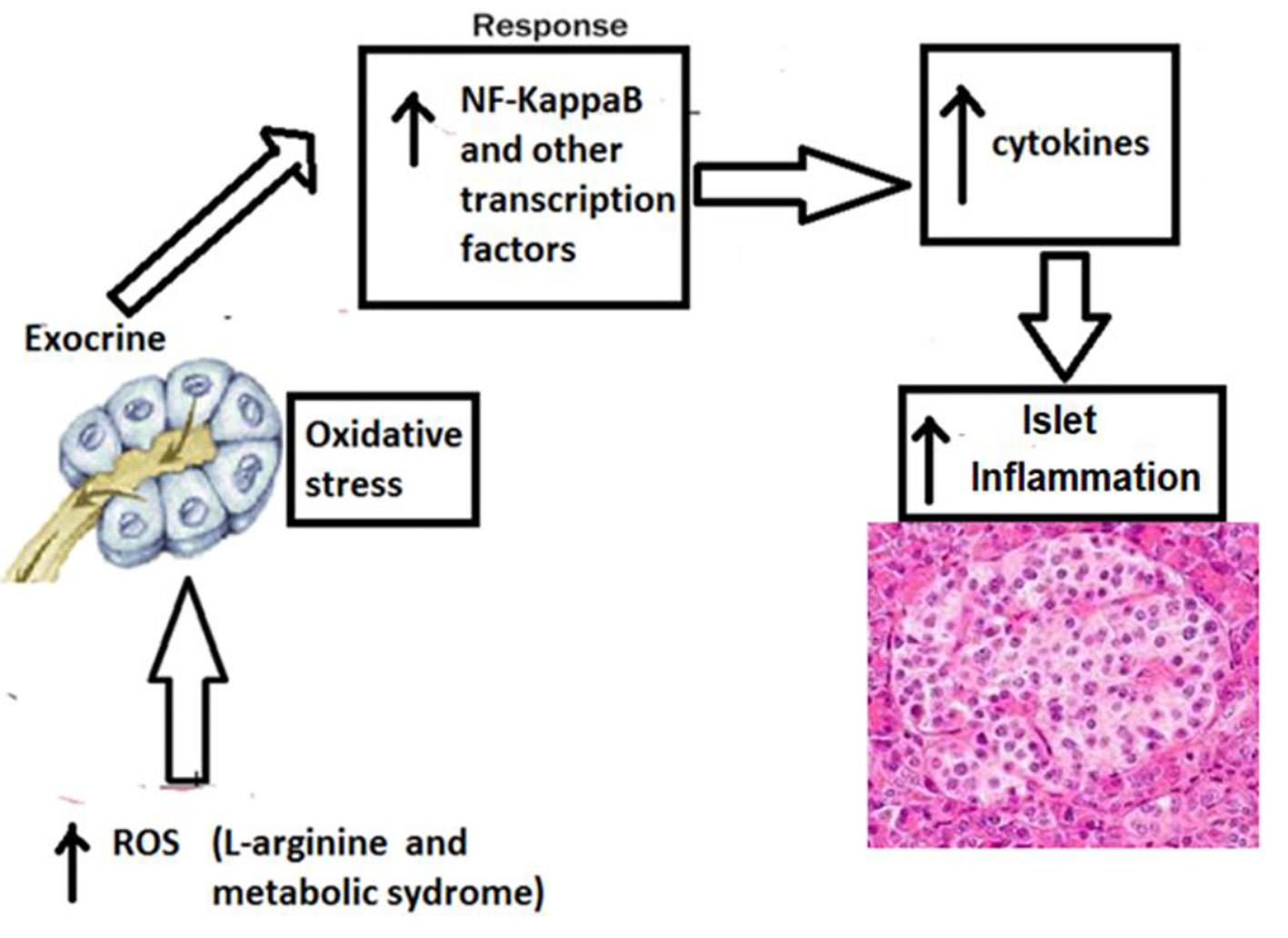
Figure 2. Mechanism of higher islet inflammation in WNIN-obese rats with acute pancreatitis. The participation of several confounding factors in the pancreatic milieu that collectively coprecipitates for a state of profound inflammation and oxidative stress in the pancreas (among mutant compared to lean/control) which gets worsened with age. These include hypertrophy, macrophage infiltration (CD11b/TNF-α/IL-6), apoptosis, β-cell vacuolation, HI, and stress markers (RL-77/HSP104/TBARS), all of which correlated well with indices for obesity (2 - 3 fold), IR (1.5 - 3 fold), and HI (2 - 3 fold). Further, supportive data were also obtained from in vitro studies using islet cell cultures amongst phenotypes. Taken together, these results advocate that oxidative stress and inflammation were the major precipitating factor to cause islet cell dysfunctions (in situ and in vitro) in these mutant rats compared to their lean littermates and parental control [2]. TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-6: interleukin-6; HI: hyperinsulinemia; IR: insulin resistance.

